A Deep Dive to AWS Cloud Security
 Image Source (varmour.com/blog/cloud-security-do-you-know..)
Image Source (varmour.com/blog/cloud-security-do-you-know..)
The understanding of AWS Security compliance and consideration of the security tools gives a customer confidence to build on AWS Cloud. It adds a customer the visibility to monitor, and spot issues before they occur. AWS Security understanding helps you to improve in security posture and attract customer trust to your business.
AWS security is based on two states:
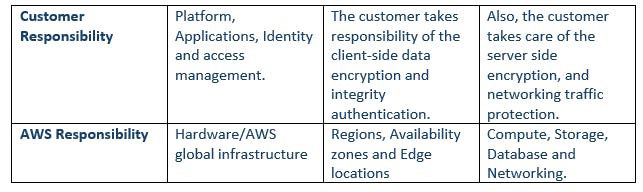
Shared responsibility and unshared responsibility between the customer and AWS. When a customer moves data into the cloud, it becomes a shared responsibility between the customer and AWS. Majorly, AWS takes the responsibility for the underlying infrastructure while the customer is responsible for the data, and applications put or connected on the cloud.
AWS Security Tools can be classified into:
1. Infrastructure Security- this concerns infrastructure network
AWS build network firewalls into Amazon VPC which creates private network and control access to instances. Provides connectivity option to enable connections from on-premise devices. AWS provides DDoS mitigation techniques at layers 3, 4, and 7. AWS provides automatic encryption of traffic on the AWS global and regional network between AWS secured facilities.
2. Inventory and configuration management
This management allows the deployment of tools to manage the creation of AWS resources according to the client’s standards. Further, a client can use the configuration tools to identify AWS resources, track and manage changes. Configuration management tools create standards and preconfigured, hardened virtual machines for EC2 instances. Another major security feature in AWS cloud service is data encryption, which allows customers to provide scalable and efficient encryption features by adding a security layer to data at rest in the cloud.
3. Data encryption
Data encryption applies to many AWS services such as Amazon EBS, Amazon S3, Amazon RDS, Amazon Redshift, Amazon ElastiCache, AWS Lambda, and Amazon SageMaker. A customer can use the flexible key management options like AWS Key Management Service which offers the option of controlling personal keys or letting AWS manage the keys on behalf. AWS provides CloudHSM which offers dedicated hardware-based cryptographic key storage. A client can trust the AWS security when transferring sensitive data because of the Amazon SQS service which resides on the server-side encryption. It’s possible to integrate encryption and data protection APIs when deploying services in the cloud.
4. Identity and Access control
AWS Directory Service this service allows customers to integrate with corporate directories to lower administrative tasks but increase user experience. AWS Single Sign-On service to centrally manage SSO access and user permissions to all accounts within the organization. AWS Identity Access Management (IAM) IAM roles let customers define individual user accounts with permissions across AWS resources. IAM works for Multi-Factor Authentication for privileged accounts.
5. Monitoring and Logging
Monitoring and logging tools include the tools which enable a client to see the activities in the AWS environment. AWS CloudTrail helps in monitoring the AWS deployments in the cloud by getting the history of AWS API calls for an account. A user can get logs via the AWS Management Console, AWS SDKs higher-level AWS service, and command-line tools. Amazon CloudWatch this service provides an automatic reliable scalable and flexible monitoring solution. Amazon GuradDuty is a threat detection service to continually monitor malicious activities and unauthorized behavior within the account. It gives notifications via Amazon CloudWatch to enable triggering of an automated response or even notify the user.
Enjoy the read. Tech-editor Nick